How do LEDs work
LEDs are semiconductor devices which convert electricity into visible light.
When powered (direct polarization), the electrons move through the semiconductor, and some of them fall in a lower energy band. Throughout the process, the energy “saved” is emitted as light.
Technical specifications of LED lights
• Crystal layers treated by chemical vapour deposition (wafer)
• A number of layers are then selected based on their luminosity and colour temperature (chip)
• The chip is mounted on a support to dissipate heat and add current continuity to the system (package)
• Electrical connection
• Lens support
• Protection against external stress
• The rear side of the package emits heat, the front emits light
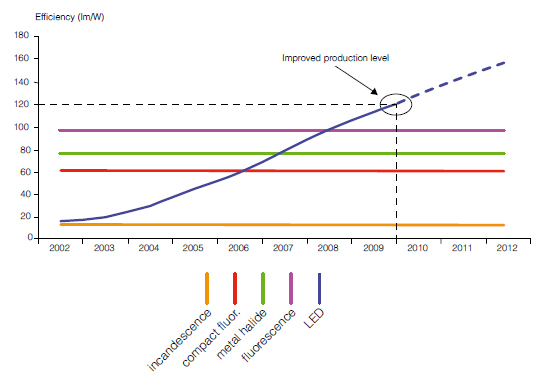
Technological research has allowed to achieve 161 lm/W for each high voltage LED.
Although not currently in production, this level shows that the development of LED lighting technologies has not yet reached its apex.